|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
“At the very minimum, Federal
Reserve Notes to the tune of
FDR’s 1933 Gold Confiscation was a Bailout of the Federal Reserve Bank by Daniel Carr, owner/operator of Moonlight Mint and www.DC-Coin.com
President Franklin Delano Roosevelt’s 1933 executive order outlawing the private ownership of gold in the United States was arguably unconstitutional. But why did he do it ? Many historians and economists point to efforts to get the economy moving again as the reason, the theory being that people were hoarding gold and the velocity of money in circulation needed to be sped up.
But the real reason for the gold confiscation was a bailout of the privately-controlled Federal Reserve Bank. And the evidence has been printed right in front of our faces.
PAPER REPLACES SPECIE
During the 1800s, paper money was suspect in the eyes of many. Nobody would ever choose a government-issue $20 note over a $20 gold coin. Gradually during the late 1800s and early 1900s, confidence in government paper money increased to the point where it was widely accepted. People accepted the money because they felt confident they could exchange it at the US Treasury or any Federal Reserve Bank for gold at any time – it even said so on the notes. Without the gold exchange clauses printed directly on the notes, the public would have been much less likely to accept them. Silver Certificates and United States Notes circulated alongside Gold Certificates, which were legally interchangeable dollar-for-dollar.
THE “FED” AND EASY MONEY
In 1913 the Federal Reserve Bank was established and it began issuing Federal Reserve Notes the following year. Once free of the restrictions imposed by the limitations of available physical gold for coinage, the quantity of Dollars in circulation increased dramatically. The increase was mostly in the form of paper money, not specie.
The result was an economic “boom”, also known as “The Roaring Twenties” (1923-1929). But like all artificially-induced stimulus, it came to a crash in the fall of 1929. The burden of over-extended credit was the culprit. Prior to the formation of the Federal Reserve, money in circulation consisted of copper, silver, and gold coins, United States Notes, Silver Certificates, and Gold Certificates. All of these were non-interest-bearing, were issued directly by the US Treasury, and did not have any debt associated with their issuance.
Notes issued by the Federal Reserve, however, were generally lent out, with interest due. So for every Federal Reserve dollar in circulation, somebody needed that dollar to pay off a debt. During the Roaring Twenties, a lot of people took on debt, resulting in a great credit expansion. When only physical gold and silver was used as money, institutions were very cautious about lending it out because if the debtor defaulted, the creditor would be out some serious (sound) money.
But with the advent of Federal Reserve Notes, the bank was more willing to lend. And with easier qualification terms, people stepped up to the window. The increased willingness to lend was due to the fact that the item being lent out was just a piece of replaceable paper, not a hard-to-get piece of gold. Sure, the notes said “redeemable in gold” (otherwise they might have been refused in commerce). But few members of the public actually exchanged such notes for actual gold. And thus, the Federal Reserve was free to lend almost at will, with little regard for loan losses. When the interest burden of all that new credit began to weigh more-heavily on the general economy, the inevitable credit contraction led to the Stock Market Crash and the Great Depression. Everyone was suddenly reluctant to borrow, banks were reluctant to lend, and the velocity of money in circulation slowed to a crawl.
A GOLD RUN ?
The financial footing of the United States became shaky. European countries which were holding substantial quantities of US gold-clause notes began presenting them to exchange for physical gold. The US Government’s fixed price of gold at $20.67 per troy ounce had been in effect for some time. But as the Great Depression deepened, the free-market price of gold started creeping up above that. This was an indication that confidence in gold-clause notes was starting to wane. A gold run on the Federal Reserve bank was imminent. And that was something that couldn’t be tolerated.
And the reason that a gold run couldn’t be tolerated, is that neither the Federal Reserve nor the US Treasury held anywhere near enough gold to back all the Gold Certificates and Federal Reserve Notes that were in circulation. And printing more of these notes would only erode confidence in them even further. The gold fractional-reserve system was at the end of the road.
GOLD-CLAUSE NOTES
This is a typical gold-exchange clause found on Gold Certificates issued by the US Treasury from about 1905 to 1922.
And the clause on series 1928 US Treasury Gold Certificates looked like this:
Series 1914 Federal Reserve Notes carried this gold-clause:
1928 series Federal Reserve Notes were printed with this:
HOW MANY IN CIRCULATION ?
Proof that the Federal Reserve Bank and the US Treasury were in serious trouble, that they didn’t have nearly enough gold to back the notes issued, can be found in the tables in the appendix to this article.
The total numbers of various notes issued are available from a number of sources. The appendix shows data reported in two books: “The Standard Handbook of United States Paper Money”, 6th edition (1977), by Chuck O’Donnell; and “The Comprehensive Catalog of U.S. Paper Money”, 1981 edition, by Gene Hessler.
To calculate the total face value of all gold-clause notes in circulation, it is necessary to know how many were issued, and how many may have still been around in 1933. The appendix tables do not include US Treasury Gold Certificates issued prior to 1905. Quantities of pre-1905 Gold Certificates were relatively small, and most would have been redeemed (and replaced with new notes) before 1933. The number of notes issued is known. The number surviving in 1933 can only be estimated.
According to the US Treasury, the average life span of a current $100 bill in circulation is about 7.5 years. Adjusted for inflation, one-hundred 2011 Dollars is equal to roughly five 1933 Dollars. Five Dollars in 1933 was a fair amount of money. The velocity of money in circulation was much lower then as well, especially during the Great Depression. A person receiving a $5 bill in change in 1933 would be unlikely to wad it up and casually stuff it in their pocket. They would more likely carefully squirrel it away for some other “rainy day”. So in 1933, a typical $5 bill would not get worn out as fast as a 2011 $100 bill. And larger-denomination notes would circulate even less often. Gold-clause notes would likely be the most tightly-held (and least circulated) of all types of notes, followed by Silver Certificates and US Notes (in that order). So it is probably a fair assumption that, on average, the “half-life” of gold-clause notes in circulation would be at least 20 years – meaning that after every 20 years or so, half the notes remaining in circulation would have to be replaced due to being worn out. The majority of gold-clause notes were issued shortly before 1933 during the 1928-1933 period, so they would still be in relatively new condition in 1933.
All this doesn’t account for gold-clause notes that were turned in for physical gold, even though they may have still been in good condition. But if Federal Reserve Notes were turned in while still in good condition, the notes would have simply been placed back into circulation by the Federal Reserve Bank or US Treasury. Many US Treasury Gold Certificates turned in for redemption may have actually been cancelled and not re-released into circulation.
GOLD SHORTFALL
Records indicate that the total gold reserves of the country in 1933 were 4 Billion dollars worth. And at $20.67 per troy ounce, that equates to about 6,000 metric tons of gold.
The total face value of US Treasury Gold Certificates issued from 1905 to 1928 equates to more than 16,000 metric tons of gold. Taking the generous assumption that the US Treasury did not issue more Gold Certificates than they had gold to back them, would mean that only 37.5% of all 1905-1928 Gold Certificates were still outstanding in 1933. In other words, if 37.5% of all Gold Certificates were still outstanding in 1933, the US Treasury would have just enough gold to back them.
Now the real problem is the gold-clause Federal Reserve Notes. Since these were generally re-released upon redemption (if in good condition), the only attrition in the quantity of notes outstanding would be due to replacement of worn-out notes. A conservative estimate of the total number of Federal Reserve Notes still in circulation in 1933 would be at least 75%.
The total face value of gold-clause Federal Reserve Notes issued prior to 1933 was equivalent to nearly 54,000 metric tons of gold. If 75% of them were outstanding in 1933, that would still be 40,500 metric tons of gold that the Federal Reserve Bank (and the US Treasury) didn’t have. Even taking the extremely low estimate of only 37.5% of the Federal Reserve Notes remaining, that would still be over 20,000 metric tons of gold. With US gold reserves at 6,000 tons, this would be a shortfall of 14,000 tons. But those 6,000 tons were needed to cover the US Treasury Gold Certificates. So at the very minimum, Federal Reserve Notes to the tune of 20,000 metric tons of gold were “circulating naked” in 1933.
And all of this doesn’t even include any of the bonds issued by the US Government which were typically denominated in gold as well.
Fourth Liberty Loan bond with gold clause: “… payable in United States gold coin of the present standard of value.”:
Approximately 7 billion dollars of these gold bonds were outstanding in 1933. But the total face value of every gold coin ever minted by the US Government totaled only about 2.3 billion dollars. This means that even if the US Government still had every single gold coin it had ever minted, that amount would still only be able to cover about one third of the Fourth Liberty Loan gold bonds that were outstanding in 1933. And, of course, the vast majority of those gold coins were held outside the US Government.
THE BAILOUT
So
along comes FDR. One of the very first things he did was issue executive
order 6102 which basically outlawed the private ownership of gold bullion. US
Treasury Gold Certificates were no longer legal tender when held by the
general public, unless exchanged at the US Treasury or Federal Reserve Bank
for other non-gold paper. The US Treasury could then transfer 6,000 metric
tons of gold to the Federal Reserve as a token backing for the “full faith
and credit of the United States”. Reportedly, the US Treasury sent gold
certificates to the Federal Reserve in exchange for Federal Reserve Notes. So
the net result of this exchange was that the privately-controlled Federal
Reserve Bank held US Treasury Gold Certificates backed by US Treasury gold,
while the US Treasury held Federal Reserve Notes backed by “credit”. These
actions bailed out the privately-controlled Federal Reserve bank, which as of
1933 would no longer be in danger of collapsing due to a short-fall of 20,000
or more metric tons of gold. During a “Fireside Chat” on 07 May 1933, Roosevelt basically admitted that gold-clause obligations far exceeded the amount of gold held by the US Treasury and Federal Reserve. In fact, the total gold obligations far exceeded the amount of gold in the entire world, not even counting corporate gold obligations.
“Behind government currency we have, in addition to the promise to pay, a reserve of gold and a small reserve of silver, neither of them anything like the total amount of the currency.” – FDR, 07 May 1933.
In the same speech, Roosevelt outlined that the total US gold reserves amounted to between 3 and 4 billion dollars worth (4,500-6,000 metric tons), and that all the gold in all the world was valued at 11 billion dollars (16,500 metric tons). At the same time, Roosevelt admits that US Government (and Federal Reserve) gold obligations were at least 30 billion dollars worth (45,000 metric tons), and that private US corporations had promised another 60 billion dollars worth (90,000 metric tons).
Roosevelt’s 07 May 1933 Fireside Chat (the important part of the audio starts at 15:30). NOTE: I have searched the internet and all posted transcripts of the speech are missing the key phrase “neither of them anything like the total amount of the currency”. But that statement is clearly heard in the audio.
As citizens complied with the new ”law” by turning in gold, the gold reserves of the US Treasury and Federal Reserve increased. After most of the public’s gold was turned in, FDR raised the official price from $20.67 to $35.00 per troy ounce. How “convenient”. Gold-clause Federal Reserve notes were not recalled and remained in circulation. But they could no longer be exchanged for gold, except by certain foreign central banks. Those with connections were able to buy valuable assets with mere paper. Wealth was concentrated in fewer hands.
The new series of
1934 Federal Reserve notes no longer had any gold clause.
The US Government also essentially defaulted on the Fourth Liberty Loan gold bonds. The bond holders had loaned money to the US Government on the basis of being paid back in gold at the rate of $20.67 per troy ounce. But when FDR revalued gold to $35 per troy ounce, the 7 billion dollars in outstanding Liberty Loan gold bonds were instantly diluted by 41%. This was equivalent to an aggregate loss of 139 million troy ounces of gold (4,325 metric tons), from the point of view of the bond holders.
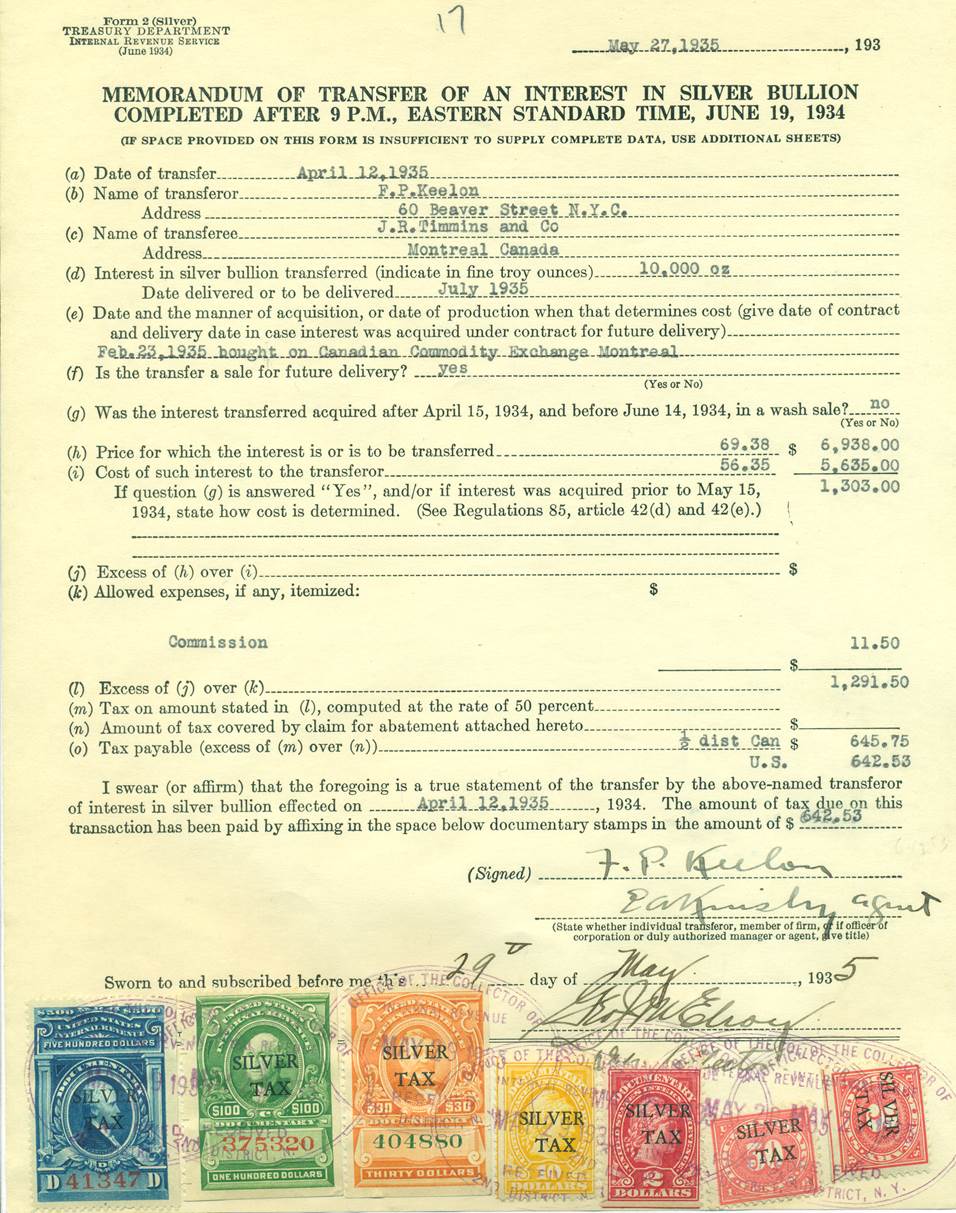
But negating gold obligations and confiscating gold wasn’t enough. The people and entities responsible for this fiasco were concerned that the public would reject the new un-backed paper money and continue the bank runs by switching to silver bullion. A recall of currently-circulating silver coins was unworkable since it would be disastrous for commerce. The solution was two-fold: confiscate silver bullion; and impose a “Silver Tax”. FDR’s Executive Order 6814 required all holders of silver bullion to deliver it to the United States Treasury for coining. This order was in effect from 1934 to 1938. Any entity that made a profit on the transfer of silver bullion, had to pay a full 50% of that profit as tax. The Silver Tax Act was imposed in 1934, and lasted until 1963. During the time that silver bullion was under a confiscation order (1934-1938) the Silver Tax would still apply to any profit from a silver bullion transaction. Such transactions during that time typically involved one party that was outside the United States (usually Canada).
1935 silver tax return related to a silver bullion transaction:
THE FALLOUT
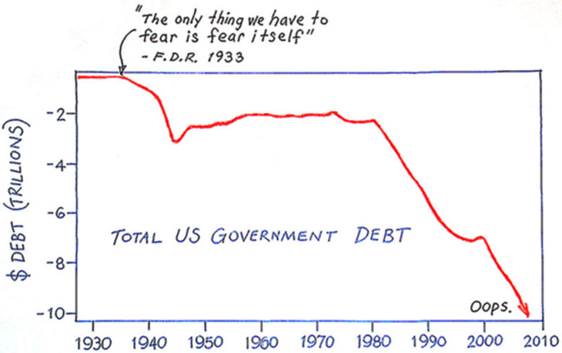
The Federal Reserve Bank’s actions, and FDR’s resulting bailout, set in motion the ultimate debt-enslavement of the US Government and its citizens.
ANOTHER GOLD CONFISCATION ?
The credit contraction which started in 2008 has many similarities to 1929. But this time, there is no gold limitation constraining the printing presses. Some people believe that another gold confiscation is a very real possibility. But the major difference between now and 1933 is that in 1933 the Federal Reserve owed a lot of gold that it didn’t have. Today the only backing for the US Dollar is the “full faith and credit” of the United States. Government debts, domestic and international, can now be paid with nothing more than newly-printed paper. The liabilities of the Federal Reserve Bank are no longer denominated in gold, and they haven’t been since Richard Nixon closed the international dollar-gold exchange window in 1971.
APPENDIX
United States Gold Obligation Gold Certificates and Federal Reserve Notes Total Face Value of Notes Issued, 1907-1933
Table Columns:
Series: Year of enactment (issue). District: Federal Reserve Bank District. $FV: Face Value of note in Dollars. Notes Issued: Total number of notes printed and issued.
The Total Face Value is the sum of the face values times the numbers of notes.
US TREASURY GOLD CERTIFICATES
Series $FV Notes Issued Total Face Value
1907 10 105,094,800 1922 10 160,604,000
1905 20 4,676,000 1906 20 55,954,587 1922 20 87,120,000
1913 50 1,624,000 1922 50 5,984,000
1922 100 2,444,000
1907 1,000 228,000 1922 1,000 80,000
1928 10 130,812,000 20 66,204,000 50 5,520,000 100 3,240,000 500 420,000 1,000 288,000 5,000 24,000 10,000 36,000
$ 10,754,999,740.00
Official US price 1933: $20.67 (per troy oz) Total gold obligation: 0.52 Billion troy oz. Total gold obligation: 16,183 Metric Tons
FEDERAL RESERVE NOTES
Series/District $FV Notes Issued Total Face Value
1914 A 5 90,400,000 B 5 297,852,000 C 5 103,824,000 D 5 73,216,000 E 5 45,932,000 F 5 54,476,000 G 5 164,876,000 H 5 41,704,000 I 5 29,280,000 J 5 43,928,000 K 5 28,536,000 L 5 91,848,000
1914 A 10 69,756,000 B 10 176,728,000 C 10 56,616,000 D 10 43,856,000 E 10 27,528,000 F 10 31,400,000 G 10 84,804,000 H 10 21,508,000 I 10 14,376,000 J 10 16,448,000 K 10 12,988,000 L 10 41,432,000
1914 A 20 25,760,000 B 20 58,704,000 C 20 30,088,000 D 20 38,544,000 E 20 16,944,000 F 20 15,956,000 G 20 46,776,000 H 20 10,748,000 I 20 6,600,000 J 20 9,172,000 K 20 6,872,000 L 20 35,756,000
1914 A 50 1,052,000 B 50 5,264,000 C 50 3,720,000 D 50 6,012,000 E 50 1,664,000 F 50 868,000 G 50 3,988,000 H 50 572,000 I 50 160,000 J 50 372,000 K 50 216,000 L 50 1,365,000
1914 A 100 728,000 B 100 3,084,000 C 100 636,000 D 100 668,000 E 100 416,000 F 100 476,000 G 100 888,000 H 100 188,000 I 100 120,000 J 100 256,000 K 100 124,000 L 100 1,064,000
1918 A 500 17,600 B 500 125,600 C 500 24,000 D 500 15,600 E 500 23,200 F 500 34,400 G 500 38,000 H 500 14,400 I 500 7,200 J 500 16,000 K 500 6,000 L 500 24,000
1918 A 1,000 39,600 B 1,000 124,800 C 1,000 16,400 D 1,000 8,800 E 1,000 17,600 F 1,000 43,200 G 1,000 23,600 H 1,000 8,400 I 1,000 7,600 J 1,000 15,200 K 1,000 6,000 L 1,000 22,400
1918 A 5,000 800 B 5,000 1,600 C 5,000 0 D 5,000 400 E 5,000 400 F 5,000 8 G 5,000 800 H 5,000 400 I 5,000 0 J 5,000 0 K 5,000 0 L 5,000 2,800
1918 A 10,000 800 B 10,000 1,600 C 10,000 0 D 10,000 400 E 10,000 400 F 10,000 0 G 10,000 0 H 10,000 400 I 10,000 0 J 10,000 0 K 10,000 0 L 10,000 2,000
1928 A 5 8,025,300 B 5 14,701,884 C 5 11,819,712 D 5 9,049,500 E 5 6,027,600 F 5 10,964,400 G 5 12,326,052 H 5 4,675,200 I 5 4,284,300 J 5 4,480,800 K 5 8,137,824 L 5 9,792,000
1928-A A 5 9,404,252 B 5 42,878,196 C 5 10,806,012 D 5 6,822,000 E 5 2,409,900 F 5 3,537,600 G 5 37,882,176 H 5 2,731,824 I 5 652,800 J 5 3,572,400 K 5 2,564,400 L 5 6,565,500
1928-B A 5 28,430,724 B 5 51,157,536 C 5 25,698,396 D 5 24,874,272 E 5 15,151,932 F 5 13,386,420 G 5 17,157,036 H 5 20,251,716 I 5 6,954,060 J 5 10,677,636 K 5 4,334,400 L 5 28,840,080
1928-C D 5 3,293,640 F 5 2,056,200 L 5 266,304
1928-D F 5 1,281,600
1928 A 10 9,804,552 B 10 11,295,796 C 10 8,114,412 D 10 7,570,680 E 10 4,534,800 F 10 6,807,720 G 10 8,130,000 H 10 4,124,100 I 10 3,874,440 J 10 3,620,400 K 10 4,855,500 L 10 7,086,900
1928-A A 10 2,893,440 B 10 16,631,056 C 10 2,710,680 D 10 5,610,000 E 10 552,300 F 10 3,033,480 G 10 8,715,000 H 10 531,600 I 10 102,600 J 10 410,400 K 10 961,800 L 10 2,547,900
1928-B A 10 33,218,088 B 10 44,458,308 C 10 22,689,216 D 10 17,418,024 E 10 12,714,504 F 10 5,246,700 G 10 38,035,000 H 10 10,814,664 I 10 5,294,460 J 10 7,748,040 K 10 3,396,096 L 10 22,695,300
1928-C B 10 2,902,678 D 10 4,230,428 E 10 304,800 F 10 688,380 G 10 2,423,400
1928 A 20 3,790,880 B 20 12,797,200 C 20 3,787,200 D 20 10,626,900 E 20 4,119,600 F 20 3,842,388 G 20 10,891,740 H 20 2,523,300 I 20 2,633,100 J 20 2,584,500 K 20 1,568,500 L 20 8,404,800
1928-A A 20 1,293,900 B 20 1,055,800 C 20 1,717,200 D 20 625,200 E 20 1,534,500 F 20 1,442,400 G 20 822,000 H 20 573,300 I 20 0 J 20 113,900 K 20 1,032,000 L 20 0
1928-B A 20 7,749,636 B 20 19,448,436 C 20 8,095,548 D 20 11,684,196 E 20 4,413,900 F 20 2,390,240 G 20 17,220,276 H 20 3,834,600 I 20 3,298,920 J 20 4,941,252 K 20 2,406,060 L 20 9,689,124
1928-C G 20 3,363,300 L 20 1,420,200
1928 A 50 265,200 B 50 1,351,800 C 50 997,056 D 50 1,161,900 E 50 539,400 F 50 538,800 G 50 1,348,620 H 50 627,300 I 50 106,200 J 50 252,600 K 50 109,920 L 50 447,600
1928-A A 50 1,834,989 B 50 3,392,328 C 50 3,078,944 D 50 2,453,364 E 50 1,516,500 F 50 338,400 G 50 5,263,956 H 50 880,500 I 50 780,240 J 50 791,604 K 50 701,496 L 50 1,522,620
1928 A 100 376,000 B 100 755,400 C 100 389,100 D 100 542,400 E 100 364,416 F 100 357,000 G 100 783,300 H 100 187,200 I 100 102,000 J 100 234,612 K 100 80,140 L 100 486,000
1928-A A 100 980,400 B 100 2,938,176 C 100 1,496,844 D 100 992,436 E 100 621,364 F 100 371,400 G 100 4,010,424 H 100 749,544 I 100 503,040 J 100 681,804 K 100 594,456 L 100 1,228,032
1928 A 500 69,120 B 500 299,400 C 500 135,120 D 500 166,440 E 500 84,720 F 500 69,360 G 500 573,600 H 500 66,180 I 500 34,680 J 500 510,720 K 500 70,560 L 500 64,080
1928 A 1,000 58,320 B 1,000 139,200 C 1,000 96,708 D 1,000 79,680 E 1,000 66,840 F 1,000 47,400 G 1,000 355,800 H 1,000 60,000 I 1,000 26,640 J 1,000 62,172 K 1,000 42,960 L 1,000 67,920
1928 A 5,000 1,320 B 5,000 2,640 C 5,000 0 D 5,000 3,000 E 5,000 3,984 F 5,000 1,440 G 5,000 3,480 H 5,000 0 I 5,000 0 J 5,000 720 K 5,000 360 L 5,000 51,300
1928 A 10,000 1,320 B 10,000 4,680 C 10,000 0 D 10,000 960 E 10,000 3,024 F 10,000 1,440 G 10,000 1,800 H 10,000 480 I 10,000 480 J 10,000 480 K 10,000 360 L 10,000 1,824
$ 35,833,509,910.00
Official US price 1933: $20.67 (per troy oz) Total gold obligation: 1.7336 Billion troy oz. Total gold obligation: 53,919 Metric Tons
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|